Unveiling the Mystery of a Ghost Plume in Oman: A New Window into Earths Interior Dynamics
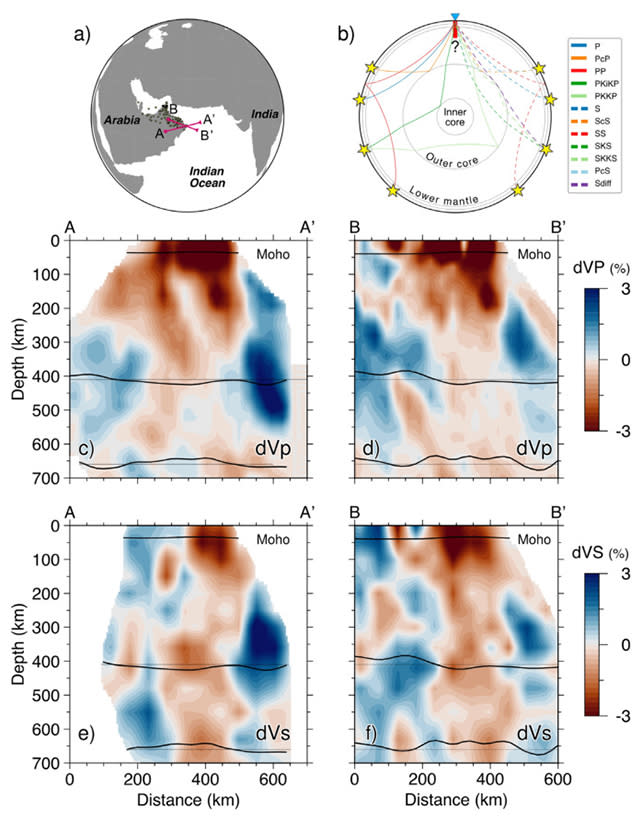
A team of scientists has made a groundbreaking discovery of a "ghost" plume beneath eastern Oman, a first-of-its-kind finding that could shed light on the interplay of heat, pressure, and movement within the Earth's interior. The plume, which rises from the Earth's core, is unusually elusive and shows no surface volcanic activity, unlike typical plumes. The discovery was made through a combination of seismic data, computer modeling, and further measurements from the field. Seismic waves slowed down as they passed through the region, suggesting the presence of hotter, softer rock below. The researchers were able to infer the hotter rock from slower seismic waves, with the plume shown in redder colors in a seismic waves chart. The plume is likely to be around 200–300 kilometers in diameter and as much as 100–300 °C (212–540 °F) hotter than the surrounding mantle. It's a relatively small, focused patch of rock that may have been around for a very long time, influencing the movement of the Indian tectonic plate some 40 million years ago. The researchers suggest that the phenomena could still be helping to elevate land in Oman today. The discovery of this "ghost" plume has implications for our understanding of plate tectonics, the evolution of life, and Earth's magnetic field. It also suggests that more heat may be leaking from the Earth's core than previously estimated, potentially requiring further studies to map out the impact of this over the long term. The findings have been published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters. The researchers emphasize that while individual results alone may appear inconclusive, their collective contribution provides a consistent and robust interpretation. If this is indeed a ghost plume, the chances are high that there are others around the world waiting to be discovered. This has implications for the models and calculations experts use to understand geological evolution. In conclusion, the discovery of this "ghost" plume is a significant step forward in our understanding of Earth's interior processes and could lead to new insights into how heat, pressure, and movement interact within our planet. The image accompanying this article shows a seismic waves chart with the "ghost" plume highlighted in redder colors, providing a visual representation of the discovery's significance.
This groundbreaking study 'Unveiling the Mystery of a Ghost Plume in Oman: A New Window into Earth's Interior Dynamics,' illustrates how cutting-edge geophysical methods unveil previously unseen insights, offering an unprecedented glimpse at our planet’slagging dynamics and subsurface process.
The intricate exploration of the mystique ghost plume in Oman, as deftly portrayed by 'Unveiling The Mystery', serves not only to shed light on a remarkable natural phenomenon but also opens an insightful window into Earth's interior dynamics and its underappreciated geological workings.