When you buy through links on our articles, Future and its syndication partners may earn a commission.
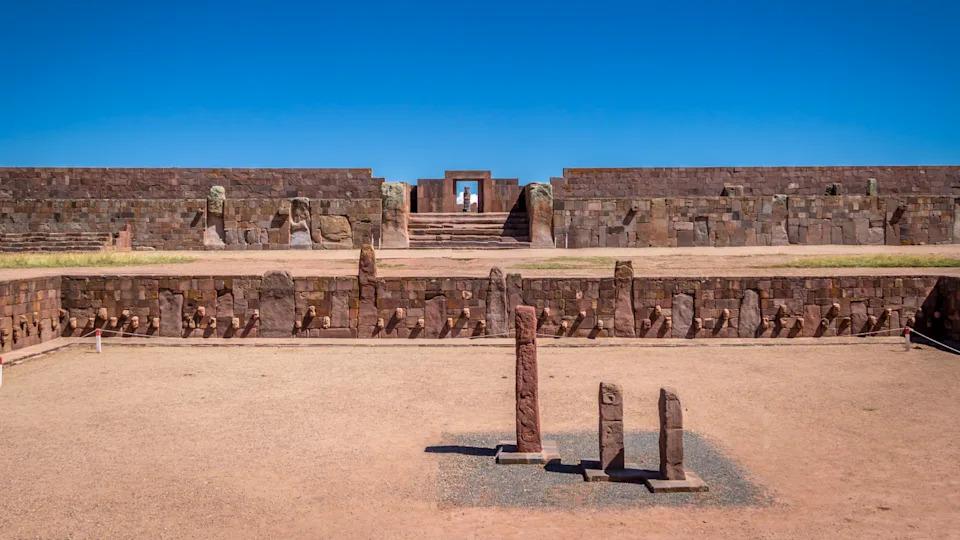 The ruins of the pre-Incan civilization at Tiwanaku near Lake Titicaca in Bolivia. | Credit: diegograndi/Getty Images
The ruins of the pre-Incan civilization at Tiwanaku near Lake Titicaca in Bolivia. | Credit: diegograndi/Getty ImagesLocated near Lake Titicaca in Bolivia, the millennia-old city of Tiwanaku was built almost 13,000 feet (4,000 meters) above sea level, making it one of the highest urban centers ever constructed.
Surrounded by mountains and hills, the city reached its peak between roughly A.D. 500 and 1000, growing to encompass an area of more than 2 square miles (6 square kilometers), organized in a grid plan. Only a small portion of the city has been excavated. Population estimates vary, but at its peak Tiwanaku may have had at least 10,000 people living in it.
Although its inhabitants didn't develop a writing system and its ancient name is unknown, archaeological remains indicate that the city's cultural and political influence was felt across the southern Andes, stretching into modern-day Peru, Chile and Argentina.
Today, with a modern-day town located nearby, Tiwanaku is a great ruin. "Massive, stone-faced earthen mounds rise from the plain; nearby are great rectangular platforms and sunken courts with beautiful cut-stone masonry," Denver Art Museum curator Margaret Young-Sánchez wrote in her book "Tiwanaku: Ancestors of the Inca" (University of Nebraska Press, 2004).
Tiwanaku origins
Researchers aren't sure when Tiwanaku was first settled, but Young-Sánchez noted in her book that people in the Lake Titicaca area started settling permanently around 4,000 years ago.
By this time, llamas (used as pack animals), alpacas (prized for their fur) and other camelids had been domesticated. In addition "farmers learned to cultivate hardy, frost-resistant crops like tubers and quinoa, watered by natural rainfall and water channeled from the mountain slopes," Young-Sánchez wrote. A millennium later, these adaptations had been enhanced by "raised-field agriculture" — a technique that "involves creating artificially raised planting mounds separated by canals of water," Young-Sánchez wrote.
These adaptations helped usher in larger and more complex settlements, one of which, Tiwanaku, would come to dominate the region.
Tiwanaku temple
In 2025, researchers announced they had found the stone ruins of a temple constructed by the Tiwanaku civilization. This temple, which archaeologists named Palaspata, is in Bolivia, about 130 miles (210 km) south of Tiwanaku.
The terraced platform temple was large — about the size of a city block — and had interior rooms that surrounded an inner courtyard. It aligned with the solar equinox and was likely used for ceremonies, according to a study published in the journal Antiquity.
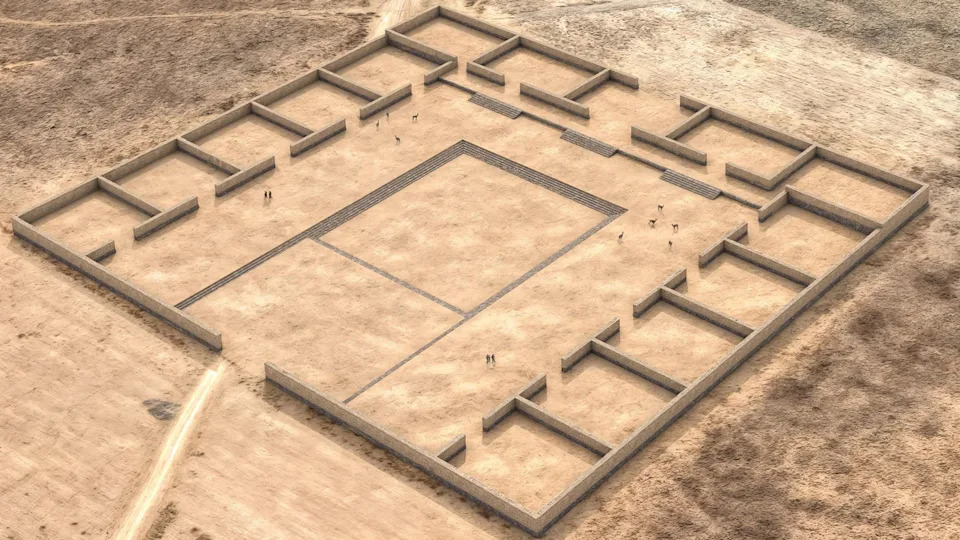 A digital reconstruction of the Palaspata temple complex, which was about the size of a city block. | Credit: José Capriles/Penn State
A digital reconstruction of the Palaspata temple complex, which was about the size of a city block. | Credit: José Capriles/Penn StateActivity at the Palaspata temple thrived from about A.D. 630 to 950, according to radiocarbon dating of charcoal found at the site. The temple's strategic location linked together three trade routes, indicating that it likely connected people in the highlands to the north, the arid plateau to the west and the valleys to the east, the researchers wrote.
The temple likely had religious connections, too, said José Capriles, an anthropological archaeologist at Penn State and lead author of the study. "Most economic and political transactions had to be mediated through divinity, because that would be a common language that would facilitate various individuals cooperating," he said in a statement.
The Tiwanaku city
Archaeological excavations have revealed that the people of Tiwanaku "maintained a dense urban population residing in well-defined, spatially segregated neighborhoods, or barrios, bounded by massive adobe compound walls," Field Museum curator Patrick Ryan Williams and team noted in a 2006 journal article
These "residential neighborhoods were characterized by multiple clusters of domestic structures (e.g., kitchens, sleeping quarters, storage facilities), some of which were apparently organized around a small private patio," the researchers added. Inhabitants of these clusters may have used larger, shared outdoor plazas for communal ceremonial events.
Archaeologists have explored much of the city center, which contains a number of monumental structures. The area " was surrounded by an artificial moat," Young-Sánchez wrote.
Sunken Temple and Kalasasaya
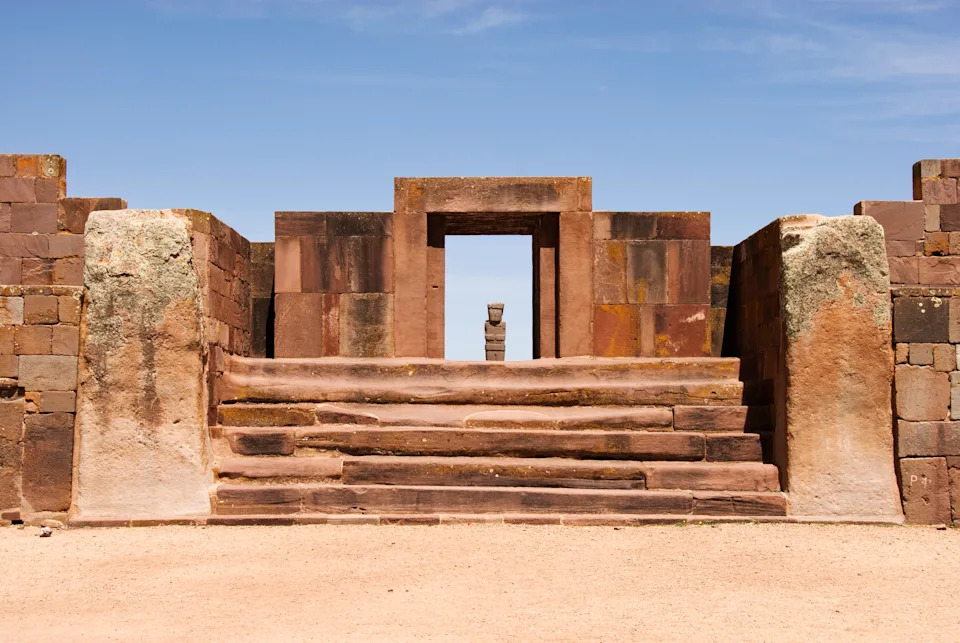 The Kalasasaya platform stands today at Tiwanaku in Bolivia. | Credit: John Elk/Getty Images
The Kalasasaya platform stands today at Tiwanaku in Bolivia. | Credit: John Elk/Getty ImagesThe area surrounded by the moat contains a number of structures that may have held religious significance.
The earliest structure is likely the "Sunken Temple," a small building that is accessed via a staircase on the south, Vanderbilt University professor John Wayne Janusek wrote in his book "Ancient Tiwanaku" (Cambridge University Press, 2008). After descending the stairs, stone monoliths can be seen in the center of the room. They depict "what were most likely the more ancient and powerful mythical ancestors of the collective communities," Janusek wrote.
The walls of the sunken temple are decorated with the images of god-like beings with expressionless faces and elaborate headdresses. Others look like "skulls with desiccated skin and sunken eye sockets, and still others appear to be wailing phantasms like the banshees of Irish lore," Janusek wrote.
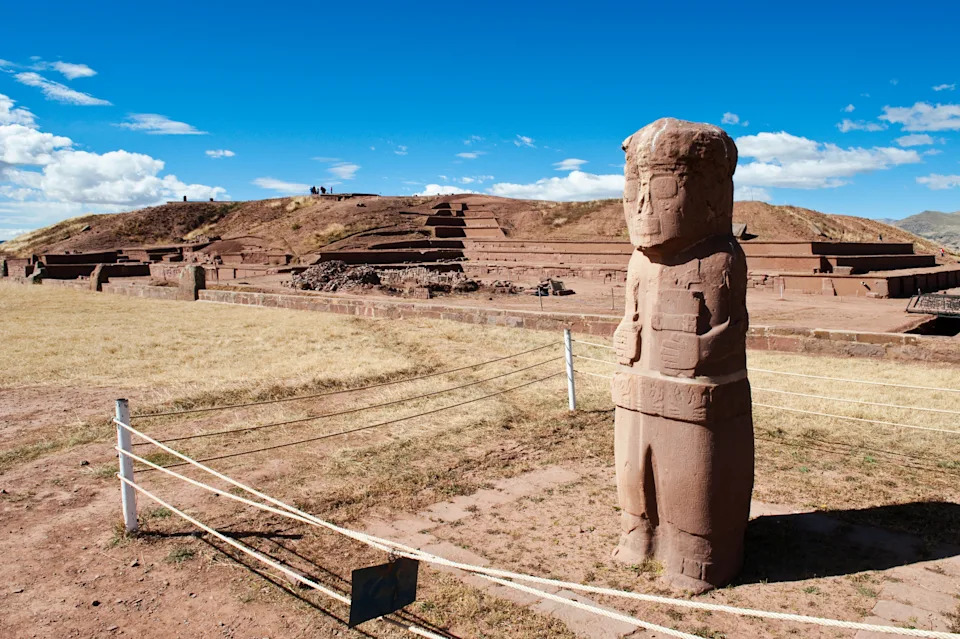 One of the carved anthropomorphic monoliths at Tiwanaku. | Credit: Atlantide Phototravel/Getty Images
One of the carved anthropomorphic monoliths at Tiwanaku. | Credit: Atlantide Phototravel/Getty ImagesAdjacent to the Sunken Temple is a platform complex known as the "Kalasasaya," researchers Brian Bauer and Charles Stanish wrote in "Ritual and Pilgrimage in the Ancient Andes: The Islands of the Sun and the Moon," (University of Texas Press, 2001).
Akapana: An artificial pyramid
An "artificial pyramid" known as the Akapana also resides in the area surrounded by the moat. This monument had six stone terraces, a massive 656 by 820 feet (200 by 250 m) base and was more than 54 feet (16.5 m) high, according to Bauer and Stanish's book. The Akapana dwarfed all other buildings at Tiwanaku and was likely a center of political and sacred power.
When archaeologists excavated the northwest portion of the pyramid, they unearthed the skeletons of 21 people, who may have been from groups Tiwanaku conquered, according to Young-Sánchez's book. Several of the bones bear deep cut marks that suggest the bodies were hacked apart just before or soon after death, before being buried at the pyramid's base, according to the book.
Pumapunku: An unfinished platform
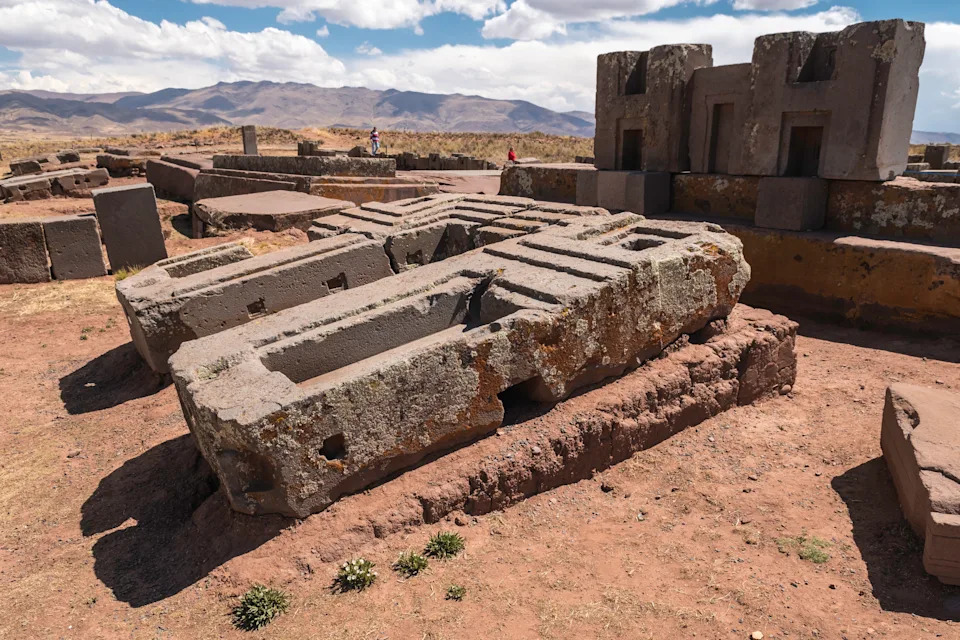 Credit: florentina georgescu photography/Getty Images
Credit: florentina georgescu photography/Getty ImagesOutside of the moat area, and located to the southwest, is a massive, unfinished platform known as the Pumapunku (also spelled Puma Punku). The main platform was nearly 1,600 feet (488 m) wide and was covered with overlapping T-shaped terraces, according to Janusek's book.The main entranceway was on the west side. "One moved up the stairway through stone portals, some covered with lintels carved as totora reed bundles and into a narrow, walled, passage" Janusek wrote. This passage then led to an "inner courtyard" with a "sunken paved patio."
Janusek noted that water seems to have played a central role in the rites that took place on the platform. The Choquepacha spring, which is southwest of the structure, has stone conduits built around it.
Decline and rebirth
Around A.D. 1000, Tiwanaku fell into decline, and the city was eventually abandoned. It collapsed around the same time the Wari culture, based to the west in what is now Peru, also fell. The timing has led scientists to wonder whether environmental change in the Andes played a role in the collapse of both civilizations.
But while Tiwanaku was abandoned, its memory lived on in the mythology of the people of the Andes.
"Even after its abandonment, Tiwanaku continued to be an important religious site for the local people," s archaeologist Alexei Vranich wrote in an "Archaeology" magazine article. It later became incorporated into Inca mythology as the birthplace of humankind, Vranich wrote, and the Inca built their own structures alongside the ruins.
Editor's note: this article was originally published on Feb. 1, 2013 and updated on July 3, 2025 to include information about the newfound Palaspata temple in Bolivia.